VPC Fundamentals
I. VPC & Subnets PrimerIV. Three Tier Architecture
- VPC: private network to deploy your resources (regional resorce)
- Subnets allow you to partition your network inside your VPC (Availability Zone resource)
- A public subnet is a subnet that is accessible from the internet
- A private subnet is a subnet that is not accessible from the internet
- To define access to the internet and between subnets, we use the Routes Tables
- Internet Gateways helps our VPC instances connect with the internet
- Public Subnets have a route to the internet gateway
- NAT Gateways (AWS-manged) & NAT instances (self-managed) allow your instances in your Private Subnets to access the internet while remaining private
Network ACL & Security Groups
- NACL (Networl ACL)
- A firewall which control traffics from and to subnet
- Can have ALLOW and DENY rules
- Are attached at the subnet level
- Rules only include IP addresses
- Security Groups
- A firewall that controls traffic to and from an ENI / an EC2 instance
- Can have only ALLOW rules
- Rules include IP addresses and other security groups
- Capture information about IP traffic going into your interfaces:
- VPC Flow Logs
- Subnet Flow Logs
- Elastic Network interface Flow Logs
- Helps to monitor & troubleshoot connectivity issues. Example:
- Subnets to internet
- Subnets to subnets
- Internet to subnets
- Captures network information from AWS managed interfaces too: Elastic Load Balancers, ElastiCache, RDS, Aurora, etc...
- VPC Flow logs data can go to S3, CloudWatch Logs, and Kinesis Data Firehose
II. VPC Peering, Endpoints, VPN, DX
1. VPC Peering
- Connect two VPC, privately using AWS' network
- Make them behave as if they were in the same network
- Must not have overlapping CIDR (IP address range)
- VPC Peering connection is not transitive (must be established for each VPC that need to communicate with one another)
- Endpoint allow you to connect to AWS services using a private network instead of the public www network
- This gives you enhanced securiry and lower latency to access AWS services
- VPC Endpoint Gateway: S3 & DynamoDB
- VPC Endpoint Interface: the rest
- Only uses within your VPC
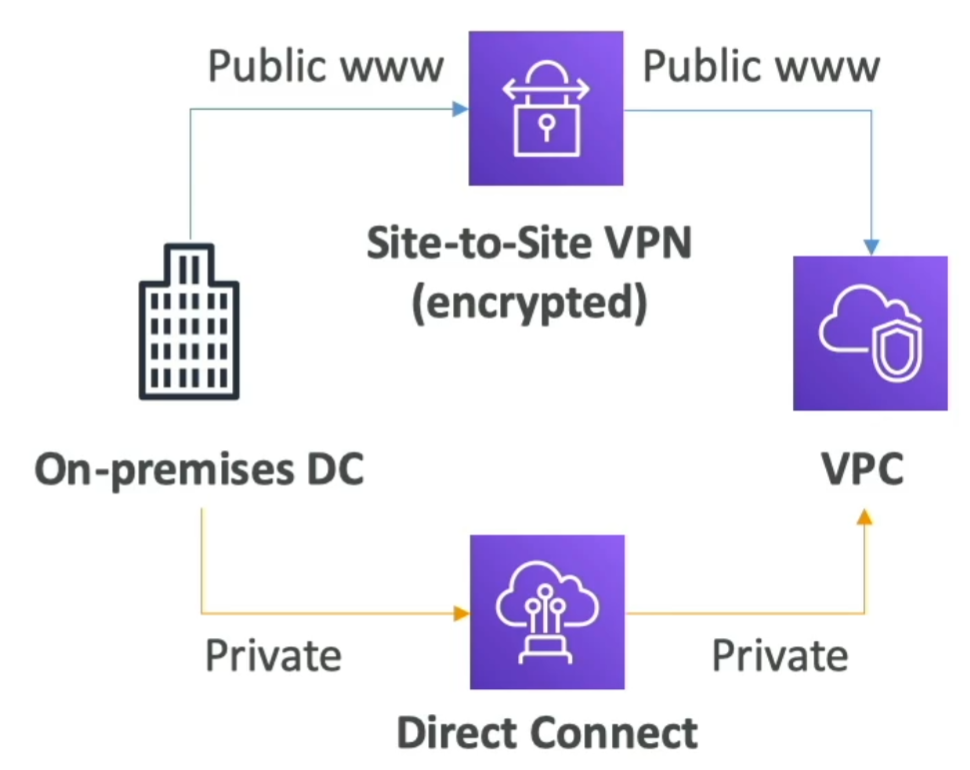
- Site to Site VPN
- Connect an on-premises VPN to AWS
- The connection is automatically encrypted
- Goes over the public internet
- Direct Connect (DX)
- Establish a physical connection between on-premises and AWS
- The connection is private, secure and fast
- Goes over a private internet
- Takes at least a month to establish
- VPC: Virtual Private Cloud
- Subnets: Tied to an AZ, network partition of the VPC
- Internet Gateway: at the VPC level, provide Internet Access
- NAT Gateway / Instances: give internet access to private subnets
- NACL; stateless, subnet rules for inbound and outbound
- Security Groups: Stateful, operate at the EC2 instance level or ENI
- VPC Peering: Connect two VPC with non overlapping IP ranges, non transitve
- VPC Endpoints: Provide private access to AWS services within VPC
- VPC Flow logs: network traffic logs
- Site to Site VPN: VPN over public internet between on-premises DC and AWS
- Direct Connect: direct private connection to AWS
Typical 3 tier solution architecture
.png)











Comments
Post a Comment