Amazon S3 Introduction
I. S3 Overview
1. Amazon s3 Usecase
- Backup and storage
- Disaster recovery
- Archive
- Hybird Cloud storage
- Application hosting
- Media hosting
- Data lakes & big data analytics
- Softeare delivery
- Static website
2. Amazon S3 - Buckets
- Amazon S3 allows people to store objects (files) in "buckets" (directories)
- Buckets must have a globally unique name (across all regions all accounts)
- Buckets are defined at the region level
- S3 look like a global service but bucket are created in a region
- Naming convention
- No uppercase, No underscore
- 3-63 characters long
- Not an IP
- Must start with lowercase letter or number
- Must not start with the prefix xn--
- Must not end with the suffix -s3alias
3. Amazon S3 - Objects
- Objects (files) have a key
- The key is full path:
- s3://my-bucket/my_file.txt
- s3://my-bucket/my_folder1/another_folder/my_file.txt
- The key is composed of prefix + object name
- s3://my-bucket/my_folder1/another_folder/my_file.txt
- There's no concept of "directories" within buckets (although the UI will trick you to think otherwise)
- Just keys with very long names that contain slashes "/"
- Object values are the content of the body:
- Max Object Size is 5TB
- If uploading more than 5GB, must use "multi-part upload
- Metadata (list of text key / value pairs - system or user metadata)
- Tags (Unicode key / value pair - upto 10) - useful for security / lifecycle
- Version ID (if versioning is enabled)
II. S3 Hands on
III. S3 Security: Bucket Policy
1. Amozon S3 - Security
- User-based
- IAM Policies - which API calls should be allowed for a specific user from IAM
- Resource-based
- Bucket Policies - bucket wide rules from S3 console - allow cross account
- Object Access Control List (ACL) - finer grain (can be disabled)
- Bucket Access Control List (ACL) - less common ( can be disabled)
- Note: an IAM principal can access an S3 object if:
- The user IAM permissions ALLOW is OR the resource policy ALLOWS it
- AND there's no explicit DENY
- Encryption: encryp objects in Amazon S3 using encryption keys
2. S3 Bucket Policies
- JSON based policies
- Resources: buckets and objects
- Effect: Allow / Deny
- Actions: Set of API to Allow or Deny
- Principal: The account or user to apply the policy to
- Use S3 bucket for policy to:
- Grant public access to the bucket
- Force objects to be encrypted at upload
- Grant access to another account (Cross account)
V. S3 Website Overview
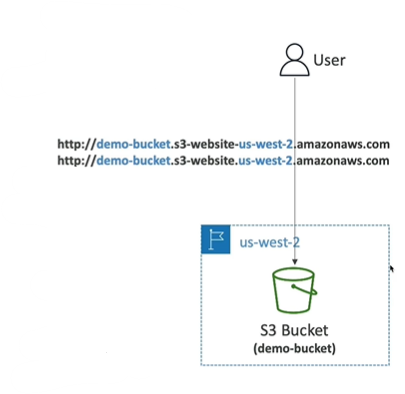
Amazon S3 - Static website Hosting
- S3 can host static websites and have them accessible on the internet
- The website URL will be (depending on the region)
- http://bucket-name.s3-website-aws-region.amazonaws.com
- or http://bucket-name.s3-website.aws-region.amazonaws.com
- If you get a 403 Forbidden error, make sure the bucket policy allow plublic reads!
VII. S3 - Versioning
- You can version your files in Amaxon S3
- It is enabled at the bucket level
- Same key overwrite will change the "version":1,2,3,...
- It is best practice to version your buckets
- Protect against unintended deletes (ability to restore a version)
- Easy roll back to previous version
- Notes:
- Any file that is not versioned prior to enabling versioning will have version "null"
- Suspending versioning does not delete the previous versions
VIII. S3 - Versioning - Hands on
IX. S3 Replication
Amazon S3 - Replication (CRR & SRR)
- Must enable Versioning in source and destinations buckets
- Cross-Region Replication (CRR)
- Same-Region Replication (SRR)
- Buckets can be in different AWS accounts
- Copying is asynchronous
- Must give proper IAM permissions to S3
- Use cases:
- CRR - compliance, lower latency access, replication across accounts
- SRR - log aggregation, live replication between production and test accounts
- After you enable Replication, only new objects are replicated
- Optionally, you can replicate existing objects using S3 Batch Repliaction
- Replicates existing objects and objects that failed replication
- For DELETE operations
- Can replicate delete markers from source to target (optional settiing)
- Deletions with a version ID are not replicated ( to avoid malicious deletes)
- There is no "chaining" of replication
- If bucket 1 has replication into bucket 2, bucket 2 has replication into bucket 3
- Then objects created in bucket 1 are not replicated to bucket 3
X. S3 Replication - Hands on
XI. S3 Storage Classes Overview
- Amazon S3 Standard - General Purpose
- Amazon S3 Standard-infrequent Access (IA)
- Amazon S3 One Zone-infrequent Access
- Amazon S3 Glacier Instant Retrieval
- Amazon S3 Glacier Flxible Retrieval
- Amazon S3 Glacier Deep Archive
- Amazon S3 Intelligent Tiering
- => Can move between classes manually or using S3 Lifecycle configurations
1. S3 Durability and Availability
- Durablility:
- Hight durablility (99.999999999% | | 9's) of objects across multiple AZ
- If you store 10,000,000 objects with Amazon S3, you can average expect to incur a loss of a single object one every 10,000 years
- Same for all storage classes
- Availability:
- Measures how readily available a services is
- Varies depending on storage class
- Example: S3 standard has 99.99% availability = not available 53 minutes a year
2. S3 Standard - General Purpose
- 99.99% Availability
- Used for frequently accessed data
- Low latency and hight throughput
- Sustain 2 concurrent facility failures
- Use cases: Big Data analytics, mobile & gaming applications, content distribution, ...
3. S3 Storage Classes - Infrequent Access
- For data that is less frequently accessed, but requires rapid access when needed
- Lower cost than S3 Standard
- Amazon S3 Standard-infrequent Access (S3 Standard-IA)
- 99.9% Availability
- Use cases: Disaster Recovery, backups
- Amazon S3 One Zone-Infrequent Access (S3 One Zone IA)
- Hight durability (99.999999999%) in a single AZ; data lost when AZ is destroyed
- 99.5% Availability
- Use cases: Storing secondary backup copies of on-premise data, or data you can recreate
4. Amazon S3 Glacier Storage Classes
- Low-cost object storage mean for archiving / backup
- Pricing: price for storage + object retrieval cost
- Amazon S3 Glacier Instant Retrieval
- Milisecond retrieval, great for data access once a quarter
- Minimum storage duration of 90days
- Amazon S3 Glacier Flexible Retrieval (formerly Amazon S3 Glacier)
- Expedited (1 to 5 minutes), Standard (3 to 5 hours), Bulk (5 to 12 hours) -free
- Minimum storage duration of 90days
- Amazon S3 Glacier Deep Archive - for long term storage:
- Standard (12 hours), Bulk (48 hours)
- Minimum storage duration of 180days
5. S3 Intelligent - Tiering
- Small monthly monitoring and auto-tiering free
- Move objects automatically between Access Tiers based on usage
- There are no retrieval charges in S3 Intelligent Tiering
- Frequent Access Tier (automatic): default tier
- Infrequent Access Tier (automatic): objects not accessed for 30days
- Archive Instant Access Tier (automatic): objects not accessed for 90days
- Archive Access Tier (optional): configurable from 90 days to 700 + days
- Deep Archive Access Tier (optional): config from 180days to 700+ days
6. S3 Storage Classes Comparison
7. S3 Storage Classes - PriceComparison
example: us-east-1
.png)













Great information, thank you for sharing the valuable article with us.
ReplyDeleteLeading DevOps Services in India.